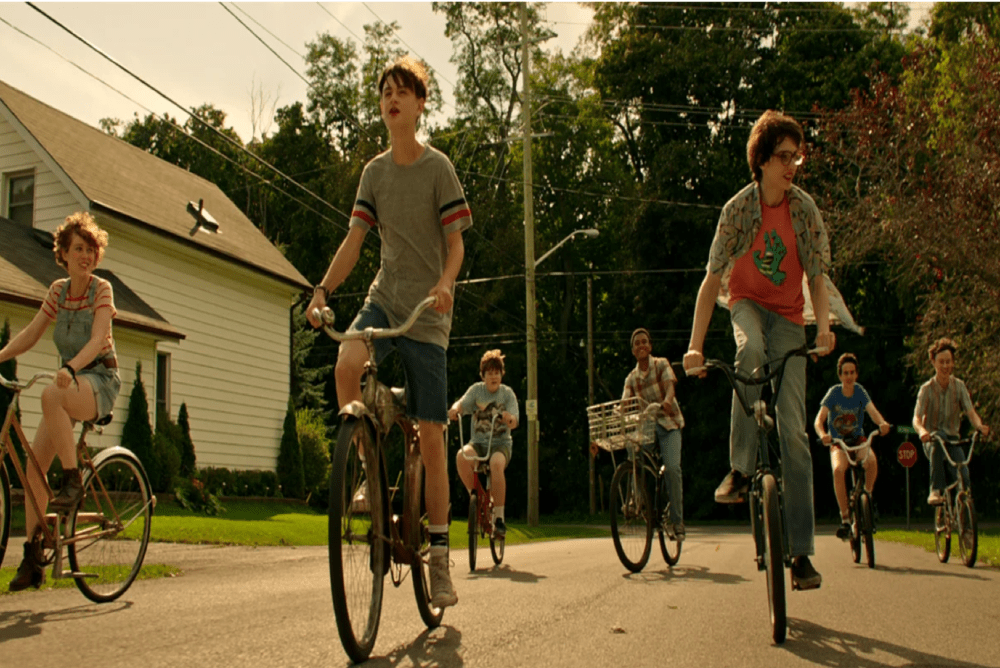Stephen King’s IT – and, later, the Andy Muschietti adaptations – have been vital to my journey as a horror fan and an aspiring fantasy/horror writer, and as an important way to think about change. I read IT during the summer of 2018, after moving from the home I had lived in for 12 years. While I approached the novel thinking I had hit the jackpot of horror, I found myself more moved by the strong bond that the Losers’ Club formed as adolescents, which made the disintegration of these friendships in adulthood all the more tragic. In many ways, IT shares more DNA with Stand By Me (a non-horror adaptation, based on King’s short story “The Body”) than some of his other horror novels. Both works are coming-of-age stories that see seemingly unshakeable friendships tested by fears and anxieties – some are explicitly horror-related, such as Pennywise, but others are more existential: how long will we remain friends? Adulthood, in these stories, seems to be more of a source of horror – or, at least, anxiety – than any monster or bully, and yet when it comes, it happens gradually. Adulthood’s arrival is not heralded by ominous music or a jumpscare, it just… happens, and childhood friendships that seemed strong don’t always last. Read more
In our hands: embers embers embers
just waiting for
the opportunity
to ignite
-Amanda Lovelace, The Witch Doesn’t Burn in This One (53)
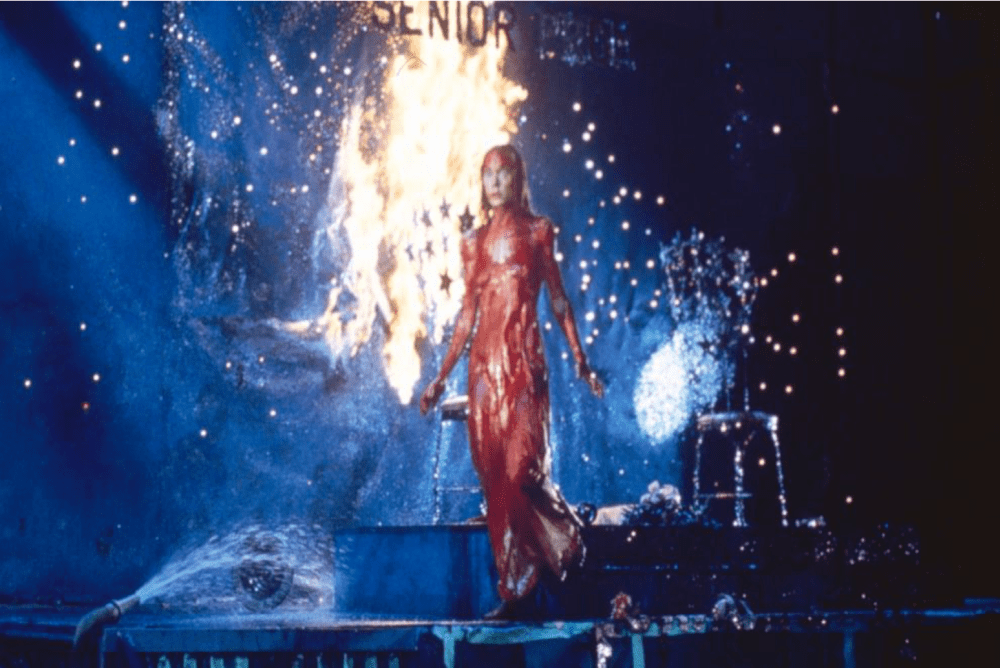
The Witch in Popular Culture
In the twenty-first century, literature and film have demonstrated a compulsion to return to the figure of the witch. Witches are embedded in popular culture old and new. From the folkloric enchantresses Baba Yaga, Circe, and Morgan Le Fay to the fairytale hags who eat, kidnap, and murder children in stories such as Hansel and Gretel, Rapunzel, and Snow White, the witch is designed to reinforce men’s fear and abhorrence towards women. Modern media, however, continues to challenge the witch as a figure of absolute terror and evil. What happens, for example, when the witch is a child herself? Portrayals of the “goodhearted” child-as-witch emerged and took centre-stage in stories such as Harry Potter (2001-11) and Chilling Adventures of Sabrina (2018). But before Hermione and Sabrina, there was Stephen King’s Carrie White.
 I started absorbing Stephen King before I was born. When she was pregnant with me, my mom distracted herself with two equally consuming tasks: stitching future-me a small quilt (despite very little knowledge or skill related to sewing) and reading the serial installments of The Green Mile, published between March and August of 1996. She spun my future with fabric squares—painstakingly arranged for comfort—and whatever textures might be taken from the echoes of chants and shaking chains on a fictional death row. Manufactured, destroyable dread was the invisible thread connecting the balloon to the toy block to the yellow background.
I started absorbing Stephen King before I was born. When she was pregnant with me, my mom distracted herself with two equally consuming tasks: stitching future-me a small quilt (despite very little knowledge or skill related to sewing) and reading the serial installments of The Green Mile, published between March and August of 1996. She spun my future with fabric squares—painstakingly arranged for comfort—and whatever textures might be taken from the echoes of chants and shaking chains on a fictional death row. Manufactured, destroyable dread was the invisible thread connecting the balloon to the toy block to the yellow background.
Now, it’s 2021 and I’m an adult who does my own grocery shopping and I see a new paperback on a display at Costco and I throw it into my cart before any food. King’s latest (aptly titled Later) is a compelling, genre-mash and in many ways, one of King’s most honest stories. Read more
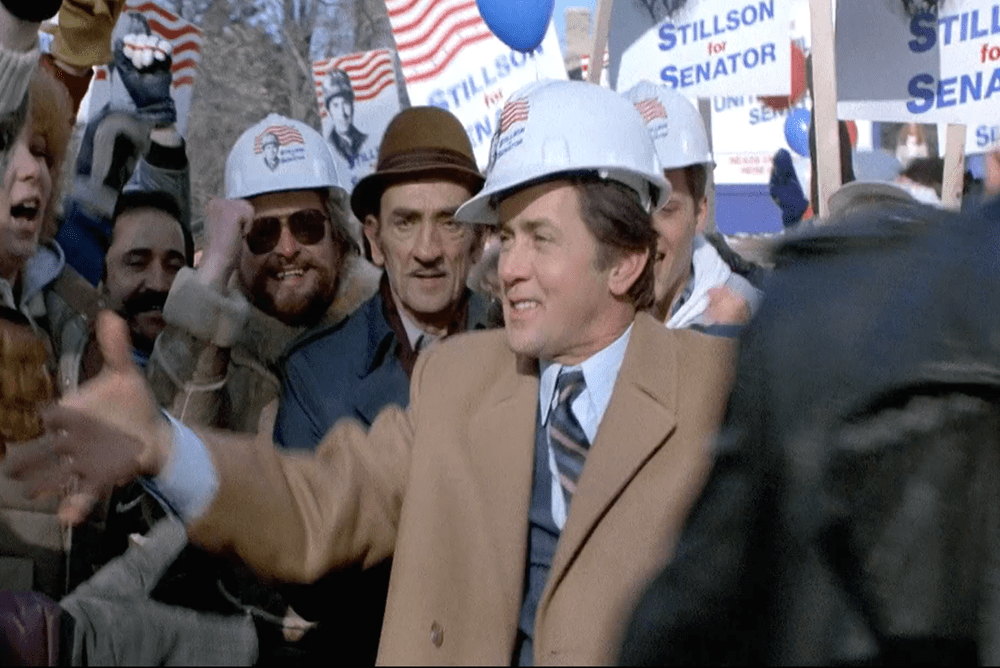
This piece aspires to be a dual-purpose essay on the feature film adaptation of Stephen King’s The Dead Zone (1983). First, I will identify qualities that make it one of the most impactful of the King inspired movies almost 40 years after its original release. In the last several years societal events have led some to reevaluate The Dead Zone and ultimately recast it as a prescient political cautionary tale about the danger posed by aspiring demagogues. My second goal is to examine that claim’s validity more closely within the context of the film as a whole. Read more
Pet Sematary, at least at the time Stephen King wrote his 2001 introduction, was the most frightening book he’d written, according to the author. He explains that for any parent the death of a child is perhaps the most traumatic event they might ever face. The only thing worse would be if s/he came back to life, not him- or herself. Two major films were made based on this novel, one in 1989, directed by Mary Lambert and a second in 2019 by Kevin Kölsch and Dennis Widmyer. Resurrection is a frightening idea. It claws out of the ground of religion.
The entire premise of resurrection, to those in the western hemisphere, derives from Christian teaching. Among the many movie monsters, two revenants in particular—the resurrected and the zombie—inspire a special fear. Is it because religion tells us that at least the former is actually possible? Horror derives much of its energy from the fear of death, and the living dead of either stripe have religious origins and cross boundaries that are carefully guarded.